Vlasov-Poisson#
In this notebook we present a multithreaded version of the Vlasov-Poisson system in 1D1D phase space. Equations are solved numerically using semi-lagrangian method.
Semi-Lagrangian method#
Let us consider an abstract scalar advection equation of the form $\( \frac{\partial f}{\partial t}+ a(x, t) \cdot \nabla f = 0. \)\( The characteristic curves associated to this equation are the solutions of the ordinary differential equations \)\( \frac{dX}{dt} = a(X(t), t) \)\( We shall denote by \)X(t, x, s)\( the unique solution of this equation associated to the initial condition \)X(s) = x$.
The classical semi-Lagrangian method is based on a backtracking of characteristics. Two steps are needed to update the distribution function \(f^{n+1}\) at \(t^{n+1}\) from its value \(f^n\) at time \(t^n\) :
For each grid point \(x_i\) compute \(X(t^n; x_i, t^{n+1})\) the value of the characteristic at \(t^n\) which takes the value \(x_i\) at \(t^{n+1}\).
As the distribution solution of first equation verifies $\(f^{n+1}(x_i) = f^n(X(t^n; x_i, t^{n+1})),\)\( we obtain the desired value of \)f^{n+1}(x_i)\( by computing \)f^n(X(t^n;x_i,t^{n+1})\( by interpolation as \)X(t^n; x_i, t^{n+1})$ is in general not a grid point.
Eric Sonnendrücker - Numerical methods for the Vlasov equations
import sys
if sys.platform == "darwin":
%env CC='gcc-10'
Bspline#
The bspline function return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
Implemented recursively using the de Boor’s recursion formula
De Boor’s Algorithm - Wikipedia
import numpy as np
from scipy.fftpack import fft, ifft
def bspline_python(p, j, x):
"""Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"""
assert (x >= 0.0) & (x <= 1.0)
assert (type(p) == int) & (type(j) == int)
if p == 0:
if j == 0:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
else:
w = (x - j) / p
w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
return w * bspline_python(p - 1, j, x) + (1 - w1) * bspline_python(p - 1, j + 1, x)
class Advection:
""" Class to compute BSL advection of 1d function """
def __init__(self, p, xmin, xmax, ncells, bspline):
assert p & 1 == 1 # check that p is odd
self.p = p
self.ncells = ncells
# compute eigenvalues of degree p b-spline matrix
self.modes = 2 * np.pi * np.arange(ncells) / ncells
self.deltax = (xmax - xmin) / ncells
self.bspline = bspline
self.eig_bspl = bspline(p, -(p + 1) // 2, 0.0)
for j in range(1, (p + 1) // 2):
self.eig_bspl += bspline(p, j - (p + 1) // 2, 0.0) * 2 * np.cos(j * self.modes)
self.eigalpha = np.zeros(ncells, dtype=complex)
def __call__(self, f, alpha):
"""compute the interpolating spline of degree p of odd degree
of a function f on a periodic uniform mesh, at
all points xi-alpha"""
p = self.p
assert (np.size(f) == self.ncells)
# compute eigenvalues of cubic splines evaluated at displaced points
ishift = np.floor(-alpha / self.deltax)
beta = -ishift - alpha / self.deltax
self.eigalpha.fill(0.)
for j in range(-(p-1)//2, (p+1)//2 + 1):
self.eigalpha += self.bspline(p, j-(p+1)//2, beta) * np.exp((ishift+j)*1j*self.modes)
# compute interpolating spline using fft and properties of circulant matrices
return np.real(ifft(fft(f) * self.eigalpha / self.eig_bspl))
def interpolation_test(bspline):
""" Test to check interpolation"""
n = 64
cs = Advection(3,0,1,n, bspline)
x = np.linspace(0,1,n, endpoint=False)
f = np.sin(x*4*np.pi)
alpha = 0.2
return np.allclose(np.sin((x-alpha)*4*np.pi), cs(f, alpha))
interpolation_test(bspline_python)
True
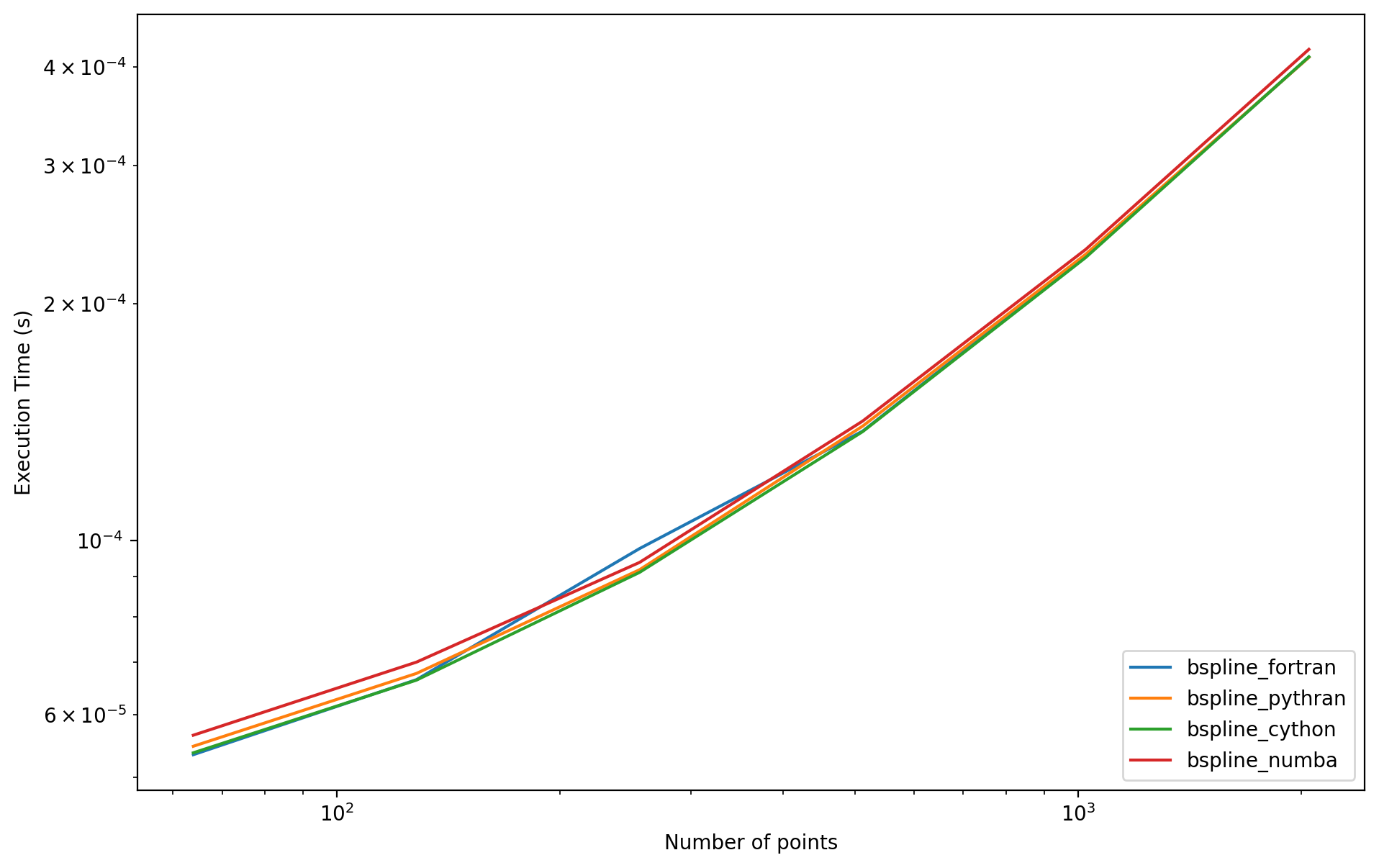
If we profile the code we can see that a lot of time is spent in bspline calls
Accelerate with Fortran#
%load_ext fortranmagic
%%fortran
recursive function bspline_fortran(p, j, x) result(res)
integer :: p, j
real(8) :: x, w, w1
real(8) :: res
if (p == 0) then
if (j == 0) then
res = 1.0
return
else
res = 0.0
return
end if
else
w = (x - j) / p
w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
end if
res = w * bspline_fortran(p-1,j,x) &
+(1-w1)*bspline_fortran(p-1,j+1,x)
end function bspline_fortran
interpolation_test(bspline_fortran)
True
Numba#
Create a optimized function of bspline python function with Numba. Call it bspline_numba.
from numba import jit, int32, float64
from scipy.fftpack import fft, ifft
@jit("float64(int32,int32,float64)",nopython=True)
def bspline_numba(p, j, x):
"""Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"""
assert ((x >= 0.0) & (x <= 1.0))
if p == 0:
if j == 0:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
else:
w = (x-j)/p
w1 = (x-j-1)/p
return w * bspline_numba(p-1,j,x)+(1-w1)*bspline_numba(p-1,j+1,x)
interpolation_test(bspline_numba)
True
Pythran#
import pythran
%load_ext pythran.magic
%%pythran
import numpy as np
#pythran export bspline_pythran(int,int,float64)
def bspline_pythran(p, j, x):
if p == 0:
if j == 0:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
else:
w = (x-j)/p
w1 = (x-j-1)/p
return w * bspline_pythran(p-1,j,x)+(1-w1)*bspline_pythran(p-1,j+1,x)
interpolation_test(bspline_pythran)
True
Cython#
%load_ext cython
%%cython -a
def bspline_cython(p, j, x):
"""Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"""
assert (x >= 0.0) & (x <= 1.0)
assert (type(p) == int) & (type(j) == int)
if p == 0:
if j == 0:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
else:
w = (x - j) / p
w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
return w * bspline_cython(p - 1, j, x) + (1 - w1) * bspline_cython(p - 1, j + 1, x)
Generated by Cython 3.0.11
Yellow lines hint at Python interaction.
Click on a line that starts with a "+" to see the C code that Cython generated for it.
+01: def bspline_cython(p, j, x):
/* Python wrapper */ static PyObject *__pyx_pw_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_1bspline_cython(PyObject *__pyx_self, #if CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL PyObject *const *__pyx_args, Py_ssize_t __pyx_nargs, PyObject *__pyx_kwds #else PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds #endif ); /*proto*/ PyDoc_STRVAR(__pyx_doc_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_bspline_cython, "Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with \n integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.\n Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"); static PyMethodDef __pyx_mdef_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_1bspline_cython = {"bspline_cython", (PyCFunction)(void*)(__Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCallWithKeywords)__pyx_pw_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_1bspline_cython, __Pyx_METH_FASTCALL|METH_KEYWORDS, __pyx_doc_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_bspline_cython}; static PyObject *__pyx_pw_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_1bspline_cython(PyObject *__pyx_self, #if CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL PyObject *const *__pyx_args, Py_ssize_t __pyx_nargs, PyObject *__pyx_kwds #else PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds #endif ) { PyObject *__pyx_v_p = 0; PyObject *__pyx_v_j = 0; PyObject *__pyx_v_x = 0; #if !CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t __pyx_nargs; #endif CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *const *__pyx_kwvalues; PyObject *__pyx_r = 0; __Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("bspline_cython (wrapper)", 0); #if !CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL #if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS __pyx_nargs = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args); #else __pyx_nargs = PyTuple_Size(__pyx_args); if (unlikely(__pyx_nargs < 0)) return NULL; #endif #endif __pyx_kwvalues = __Pyx_KwValues_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, __pyx_nargs); { PyObject **__pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_n_s_p,&__pyx_n_s_j,&__pyx_n_s_x,0}; PyObject* values[3] = {0,0,0}; if (__pyx_kwds) { Py_ssize_t kw_args; switch (__pyx_nargs) { case 3: values[2] = __Pyx_Arg_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 2); CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH; case 2: values[1] = __Pyx_Arg_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 1); CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH; case 1: values[0] = __Pyx_Arg_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 0); CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH; case 0: break; default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error; } kw_args = __Pyx_NumKwargs_FASTCALL(__pyx_kwds); switch (__pyx_nargs) { case 0: if (likely((values[0] = __Pyx_GetKwValue_FASTCALL(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_kwvalues, __pyx_n_s_p)) != 0)) { (void)__Pyx_Arg_NewRef_FASTCALL(values[0]); kw_args--; } else if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) else goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error; CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH; case 1: if (likely((values[1] = __Pyx_GetKwValue_FASTCALL(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_kwvalues, __pyx_n_s_j)) != 0)) { (void)__Pyx_Arg_NewRef_FASTCALL(values[1]); kw_args--; } else if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) else { __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("bspline_cython", 1, 3, 3, 1); __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) } CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH; case 2: if (likely((values[2] = __Pyx_GetKwValue_FASTCALL(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_kwvalues, __pyx_n_s_x)) != 0)) { (void)__Pyx_Arg_NewRef_FASTCALL(values[2]); kw_args--; } else if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) else { __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("bspline_cython", 1, 3, 3, 2); __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) } } if (unlikely(kw_args > 0)) { const Py_ssize_t kwd_pos_args = __pyx_nargs; if (unlikely(__Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_kwvalues, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values + 0, kwd_pos_args, "bspline_cython") < 0)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) } } else if (unlikely(__pyx_nargs != 3)) { goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error; } else { values[0] = __Pyx_Arg_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 0); values[1] = __Pyx_Arg_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 1); values[2] = __Pyx_Arg_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 2); } __pyx_v_p = values[0]; __pyx_v_j = values[1]; __pyx_v_x = values[2]; } goto __pyx_L6_skip; __pyx_L5_argtuple_error:; __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("bspline_cython", 1, 3, 3, __pyx_nargs); __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) __pyx_L6_skip:; goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done; __pyx_L3_error:; { Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp; for (__pyx_temp=0; __pyx_temp < (Py_ssize_t)(sizeof(values)/sizeof(values[0])); ++__pyx_temp) { __Pyx_Arg_XDECREF_FASTCALL(values[__pyx_temp]); } } __Pyx_AddTraceback("_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86.bspline_cython", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename); __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext(); return NULL; __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:; __pyx_r = __pyx_pf_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_bspline_cython(__pyx_self, __pyx_v_p, __pyx_v_j, __pyx_v_x); int __pyx_lineno = 0; const char *__pyx_filename = NULL; int __pyx_clineno = 0; /* function exit code */ { Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp; for (__pyx_temp=0; __pyx_temp < (Py_ssize_t)(sizeof(values)/sizeof(values[0])); ++__pyx_temp) { __Pyx_Arg_XDECREF_FASTCALL(values[__pyx_temp]); } } __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext(); return __pyx_r; } static PyObject *__pyx_pf_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_bspline_cython(CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_p, PyObject *__pyx_v_j, PyObject *__pyx_v_x) { PyObject *__pyx_v_w = NULL; PyObject *__pyx_v_w1 = NULL; PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL; /* … */ /* function exit code */ __pyx_L1_error:; __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_8); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_9); __Pyx_AddTraceback("_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86.bspline_cython", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename); __pyx_r = NULL; __pyx_L0:; __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_w); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_w1); __Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r); __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext(); return __pyx_r; } /* … */ __pyx_tuple_ = PyTuple_Pack(5, __pyx_n_s_p, __pyx_n_s_j, __pyx_n_s_x, __pyx_n_s_w, __pyx_n_s_w1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple_)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple_); __Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple_); /* … */ __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_CyFunction_New(&__pyx_mdef_54_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa186643eafd1b2d5ada5bc86_1bspline_cython, 0, __pyx_n_s_bspline_cython, NULL, __pyx_n_s_cython_magic_8b355ddae92152cfa1, __pyx_d, ((PyObject *)__pyx_codeobj__2)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_d, __pyx_n_s_bspline_cython, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_d, __pyx_n_s_test, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
02: """Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
03: integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
04: Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"""
+05: assert (x >= 0.0) & (x <= 1.0)
#ifndef CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS
if (unlikely(__pyx_assertions_enabled())) {
__pyx_t_1 = PyObject_RichCompare(__pyx_v_x, __pyx_float_0_0, Py_GE); __Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_2 = PyObject_RichCompare(__pyx_v_x, __pyx_float_1_0, Py_LE); __Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_3 = PyNumber_And(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_4 < 0))) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) {
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_builtin_AssertionError, 0, 0, 0);
__PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
}
}
#else
if ((1)); else __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
+06: assert (type(p) == int) & (type(j) == int)
#ifndef CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS
if (unlikely(__pyx_assertions_enabled())) {
__pyx_t_3 = PyObject_RichCompare(((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(__pyx_v_p)), ((PyObject *)(&PyInt_Type)), Py_EQ); __Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_2 = PyObject_RichCompare(((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(__pyx_v_j)), ((PyObject *)(&PyInt_Type)), Py_EQ); __Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_1 = PyNumber_And(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_t_1); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_4 < 0))) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) {
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_builtin_AssertionError, 0, 0, 0);
__PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
}
}
#else
if ((1)); else __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
+07: if p == 0:
__pyx_t_4 = (__Pyx_PyInt_BoolEqObjC(__pyx_v_p, __pyx_int_0, 0, 0)); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_4 < 0))) __PYX_ERR(0, 7, __pyx_L1_error) if (__pyx_t_4) { /* … */ }
+08: if j == 0:
__pyx_t_4 = (__Pyx_PyInt_BoolEqObjC(__pyx_v_j, __pyx_int_0, 0, 0)); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_4 < 0))) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error) if (__pyx_t_4) { /* … */ }
+09: return 1.0
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_float_1_0); __pyx_r = __pyx_float_1_0; goto __pyx_L0;
10: else:
+11: return 0.0
/*else*/ {
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_float_0_0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_float_0_0;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
12: else:
+13: w = (x - j) / p
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_1 = PyNumber_Subtract(__pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_j); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_p); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_v_w = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
+14: w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
__pyx_t_2 = PyNumber_Subtract(__pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_j); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 14, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyInt_SubtractObjC(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_int_1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 14, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_p); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 14, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0; __pyx_v_w1 = __pyx_t_2; __pyx_t_2 = 0; }
+15: return w * bspline_cython(p - 1, j, x) + (1 - w1) * bspline_cython(p - 1, j + 1, x)
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r); __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_n_s_bspline_cython); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyInt_SubtractObjC(__pyx_v_p, __pyx_int_1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_5 = NULL; __pyx_t_6 = 0; #if CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS if (unlikely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_1))) { __pyx_t_5 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_1); if (likely(__pyx_t_5)) { PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_1); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5); __Pyx_INCREF(function); __Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_1, function); __pyx_t_6 = 1; } } #endif { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[4] = {__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_3, __pyx_v_j, __pyx_v_x}; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_callargs+1-__pyx_t_6, 3+__pyx_t_6); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0; } __pyx_t_1 = PyNumber_Multiply(__pyx_v_w, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyInt_SubtractCObj(__pyx_int_1, __pyx_v_w1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_n_s_bspline_cython); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyInt_SubtractObjC(__pyx_v_p, __pyx_int_1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_8 = __Pyx_PyInt_AddObjC(__pyx_v_j, __pyx_int_1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_8)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_9 = NULL; __pyx_t_6 = 0; #if CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS if (unlikely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_5))) { __pyx_t_9 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_5); if (likely(__pyx_t_9)) { PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_5); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_9); __Pyx_INCREF(function); __Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_5, function); __pyx_t_6 = 1; } } #endif { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[4] = {__pyx_t_9, __pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_8, __pyx_v_x}; __pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_callargs+1-__pyx_t_6, 3+__pyx_t_6); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; } __pyx_t_5 = PyNumber_Multiply(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; __pyx_t_3 = PyNumber_Add(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_t_5); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 15, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_r = __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_3 = 0; goto __pyx_L0;
%%cython
import cython
@cython.cdivision(True)
cpdef double bspline_cython(int p, int j, double x):
"""Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"""
cdef double w, w1
if p == 0:
if j == 0:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
else:
w = (x - j) / p
w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
return w * bspline_cython(p-1,j,x)+(1-w1)*bspline_cython(p-1,j+1,x)
interpolation_test(bspline_cython)
True
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (11,7)
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from collections import defaultdict
Mrange = (2 ** np.arange(6, 12)).astype(int)
opts = [bspline_fortran, bspline_pythran, bspline_cython, bspline_numba]
times = defaultdict(list)
for M in tqdm(Mrange):
x = np.linspace(0, 1, M, endpoint=False)
for opt in opts:
f = np.sin(x*4*np.pi)
cs = Advection(5, 0, 1, M, opt)
alpha = 0.1
ts = %timeit -q -n 100 -o cs(f, alpha)
times[opt.__name__].append(ts.best)
for o, t in times.items():
plt.loglog(Mrange, t, label=o)
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.xlabel('Number of points')
plt.ylabel('Execution Time (s)');
%%cython
import cython
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
from scipy.fftpack import fft, ifft
@cython.cdivision(True)
cdef double bspline_cython(int p, int j, double x):
"""Return the value at x in [0,1[ of the B-spline with
integer nodes of degree p with support starting at j.
Implemented recursively using the de Boor's recursion formula"""
cdef double w, w1
if p == 0:
if j == 0:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
else:
w = (x - j) / p
w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
return w * bspline_cython(p-1,j,x)+(1-w1)*bspline_cython(p-1,j+1,x)
class BSplineCython:
def __init__(self, p, xmin, xmax, ncells):
self.p = p
self.ncells = ncells
# compute eigenvalues of degree p b-spline matrix
self.modes = 2 * np.pi * np.arange(ncells) / ncells
self.deltax = (xmax - xmin) / ncells
self.eig_bspl = bspline_cython(p,-(p+1)//2, 0.0)
for j in range(1, (p + 1) // 2):
self.eig_bspl += bspline_cython(p,j-(p+1)//2,0.0)*2*np.cos(j*self.modes)
self.eigalpha = np.zeros(ncells, dtype=complex)
@cython.boundscheck(False)
@cython.wraparound(False)
def __call__(self, f, alpha):
"""compute the interpolating spline of degree p of odd degree
of a function f on a periodic uniform mesh, at
all points xi-alpha"""
cdef Py_ssize_t j
cdef int p = self.p
# compute eigenvalues of cubic splines evaluated at displaced points
cdef int ishift = np.floor(-alpha / self.deltax)
cdef double beta = -ishift - alpha / self.deltax
self.eigalpha.fill(0)
for j in range(-(p-1)//2, (p+1)//2+1):
self.eigalpha += bspline_cython(p,j-(p+1)//2,beta)*np.exp((ishift+j)*1j*self.modes)
# compute interpolating spline using fft and properties of circulant matrices
return np.real(ifft(fft(f) * self.eigalpha / self.eig_bspl))
Content of stderr:
In file included from /usr/share/miniconda/envs/python-fortran/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarraytypes.h:1909,
from /usr/share/miniconda/envs/python-fortran/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarrayobject.h:12,
from /usr/share/miniconda/envs/python-fortran/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/arrayobject.h:5,
from /home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_a8089a1ad99d91f89ca852660308b28608e7549e.c:1250:
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/python-fortran/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/npy_1_7_deprecated_api.h:17:2: warning: #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " "#define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION" [-Wcpp]
17 | #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " \
| ^~~~~~~
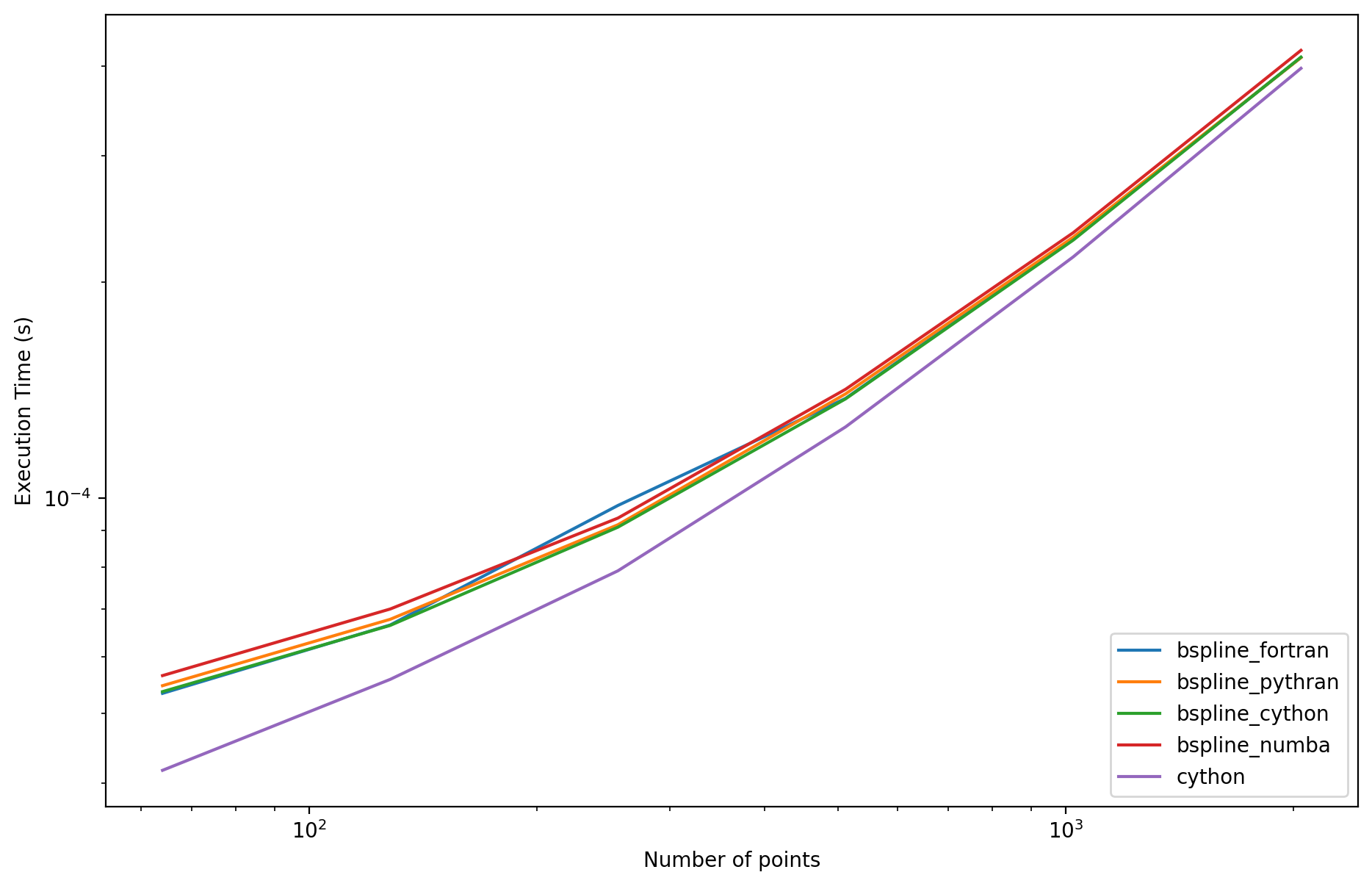
times["cython"] = []
for M in tqdm(Mrange):
x = np.linspace(0, 1, M, endpoint=False)
f = np.sin(x*4*np.pi)
cs = BSplineCython(5, 0, 1, M )
alpha = 0.1
ts = %timeit -q -n 100 -o cs(f, alpha)
times["cython"].append(ts.best)
Vlasov-Poisson system#
system for one species with a neutralizing background.
class VlasovPoisson:
def __init__(self, xmin, xmax, nx, vmin, vmax, nv, p = 3, opt=None):
# Grid
self.nx = nx
self.x, self.dx = np.linspace(xmin, xmax, nx, endpoint=False, retstep=True)
self.nv = nv
self.v, self.dv = np.linspace(vmin, vmax, nv, endpoint=False, retstep=True)
# Distribution function
self.f = np.zeros((nx,nv))
self.p = p
if opt :
# Interpolators for advection
self.cs_x = Advection(p, xmin, xmax, nx, opt)
self.cs_v = Advection(p, vmin, vmax, nv, opt)
# Modes for Poisson equation
self.modes = np.zeros(nx)
k = 2* np.pi / (xmax - xmin)
self.modes[:nx//2] = k * np.arange(nx//2)
self.modes[nx//2:] = - k * np.arange(nx//2,0,-1)
self.modes += self.modes == 0 # avoid division by zero
def advection_x(self, dt):
for j in range(self.nv):
alpha = dt * self.v[j]
self.f[j,:] = self.cs_x(self.f[j,:], alpha)
def advection_v(self, e, dt):
for i in range(self.nx):
alpha = dt * e[i]
self.f[:,i] = self.cs_v(self.f[:,i], alpha)
def compute_rho(self):
rho = self.dv * np.sum(self.f, axis=0)
return rho - rho.mean()
def compute_e(self, rho):
# compute Ex using that ik*Ex = rho
rhok = fft(rho)/self.modes
return np.real(ifft(-1j*rhok))
def run(self, f, nstep, dt):
self.f = f
nrj = []
self.advection_x(0.5*dt)
for istep in tqdm(range(nstep)):
rho = self.compute_rho()
e = self.compute_e(rho)
self.advection_v(e, dt)
self.advection_x(dt)
nrj.append( 0.5*np.log(np.sum(e*e)*self.dx))
return nrj
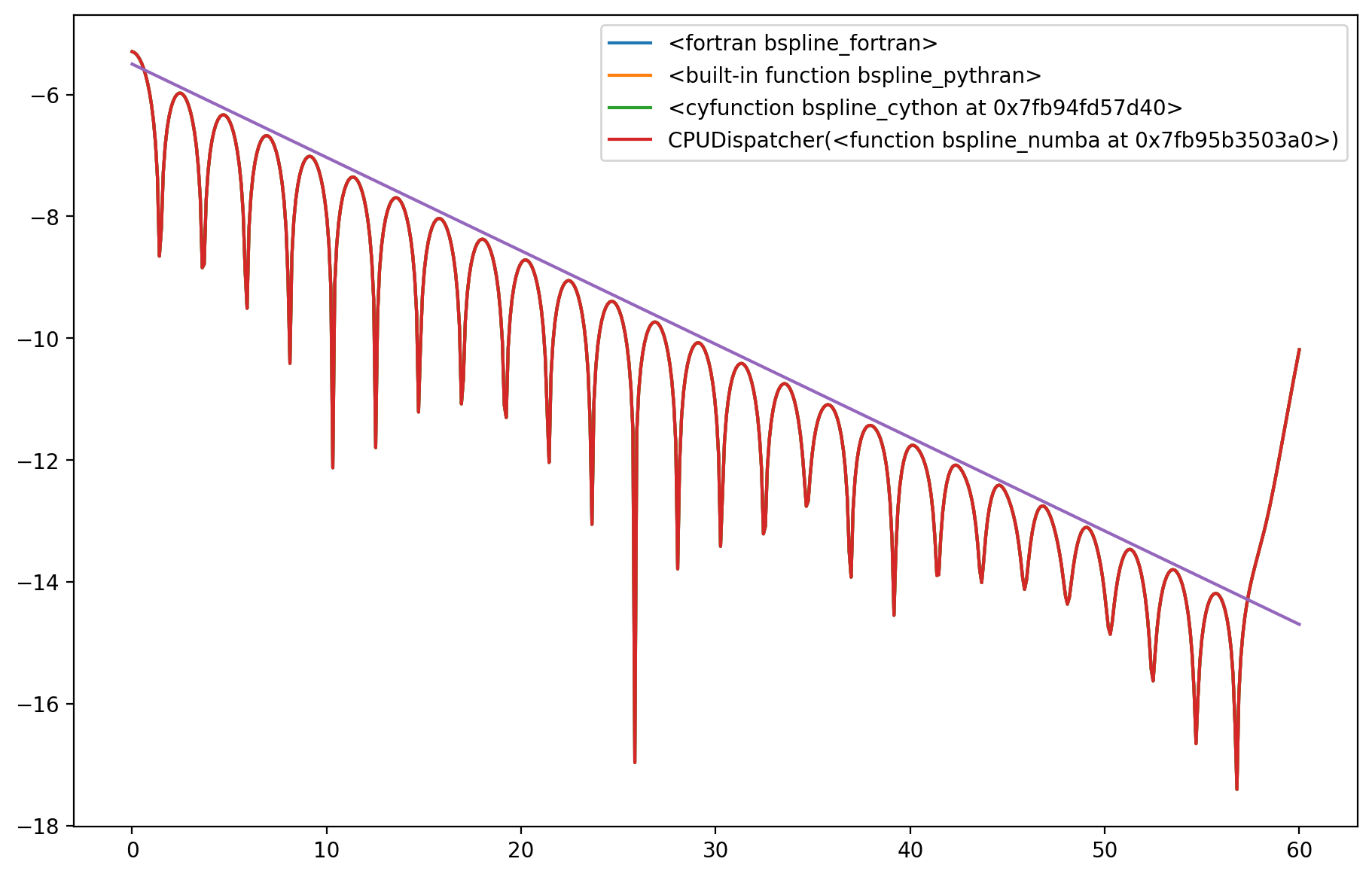
Landau Damping#
from time import time
elapsed_time = {}
fig, axes = plt.subplots()
for opt in opts:
# Set grid
nx, nv = 32, 64
xmin, xmax = 0.0, 4*np.pi
vmin, vmax = -6., 6.
# Create Vlasov-Poisson simulation
sim = VlasovPoisson(xmin, xmax, nx, vmin, vmax, nv, opt=opt)
# Initialize distribution function
X, V = np.meshgrid(sim.x, sim.v)
eps, kx = 0.001, 0.5
f = (1.0+eps*np.cos(kx*X))/np.sqrt(2.0*np.pi)* np.exp(-0.5*V*V)
# Set time domain
nstep = 600
t, dt = np.linspace(0.0, 60.0, nstep, retstep=True)
# Run simulation
etime = time()
nrj = sim.run(f, nstep, dt)
print(" {0:12s} : {1:.4f} ".format(opt.__name__, time()-etime))
# Plot energy
axes.plot(t, nrj, label=opt)
axes.plot(t, -0.1533*t-5.50)
plt.legend();
%%fortran --f90flags "-fopenmp" --extra "-lgomp" --link fftw3
module bsl_fftw
use, intrinsic :: iso_c_binding
implicit none
include 'fftw3.f03'
contains
recursive function bspline(p, j, x) result(res)
integer :: p, j
real(8) :: x, w, w1
real(8) :: res
if (p == 0) then
if (j == 0) then
res = 1.0
return
else
res = 0.0
return
end if
else
w = (x - j) / p
w1 = (x - j - 1) / p
end if
res = w * bspline(p-1,j,x)+(1-w1)*bspline(p-1,j+1,x)
end function bspline
subroutine advection(p, n, delta, alpha, axis, df)
integer, intent(in) :: p
integer, intent(in) :: n
real(8), intent(in) :: delta
real(8), intent(in) :: alpha(0:n-1)
integer, intent(in) :: axis
real(8), intent(inout) :: df(0:n-1,0:n-1)
!f2py optional , depend(in) :: n=shape(df,0)
real(8), allocatable :: f(:)
complex(8), allocatable :: ft(:)
real(8), allocatable :: eig_bspl(:)
real(8), allocatable :: modes(:)
complex(8), allocatable :: eigalpha(:)
integer(8) :: fwd
integer(8) :: bwd
integer :: i
integer :: j
integer :: ishift
real(8) :: beta
real(8) :: pi
pi = 4.0_8 * atan(1.0_8)
allocate(modes(0:n/2))
allocate(eigalpha(0:n/2))
allocate(eig_bspl(0:n/2))
allocate(f(0:n-1))
allocate(ft(0:n/2))
do i = 0, n/2
modes(i) = 2.0_8 * pi * i / n
end do
call dfftw_plan_dft_r2c_1d(fwd, n, f, ft, FFTW_ESTIMATE)
call dfftw_plan_dft_c2r_1d(bwd, n, ft, f, FFTW_ESTIMATE)
eig_bspl = 0.0
do j = 1, (p+1)/2
eig_bspl = eig_bspl + bspline(p, j-(p+1)/2, 0.0_8) * 2.0 * cos(j * modes)
end do
eig_bspl = eig_bspl + bspline(p, -(p+1)/2, 0.0_8)
!$OMP PARALLEL DO DEFAULT(FIRSTPRIVATE), SHARED(df,fwd,bwd)
do i = 0, n-1
ishift = floor(-alpha(i) / delta)
beta = -ishift - alpha(i) / delta
eigalpha = (0.0_8, 0.0_8)
do j=-(p-1)/2, (p+1)/2+1
eigalpha = eigalpha + bspline(p, j-(p+1)/2, beta) * exp((ishift+j) * (0.0_8,1.0_8) * modes)
end do
if (axis == 0) then
f = df(:,i)
else
f = df(i,:)
end if
call dfftw_execute_dft_r2c(fwd, f, ft)
ft = ft * eigalpha / eig_bspl / n
call dfftw_execute_dft_c2r(bwd, ft, f)
if (axis == 0) then
df(:,i) = f
else
df(i,:) = f
end if
end do
!$OMP END PARALLEL DO
call dfftw_destroy_plan(fwd)
call dfftw_destroy_plan(bwd)
deallocate(modes)
deallocate(eigalpha)
deallocate(eig_bspl)
deallocate(f)
deallocate(ft)
end subroutine advection
end module bsl_fftw
%env OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
env: OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from scipy.fftpack import fft, ifft
class VlasovPoissonThreaded(VlasovPoisson):
def advection_x(self, dt):
alpha = dt * self.v
bsl_fftw.advection(self.p, self.dx, alpha, 1, self.f)
def advection_v(self, e, dt):
alpha = dt * e
bsl_fftw.advection(self.p, self.dv, alpha, 0, self.f)
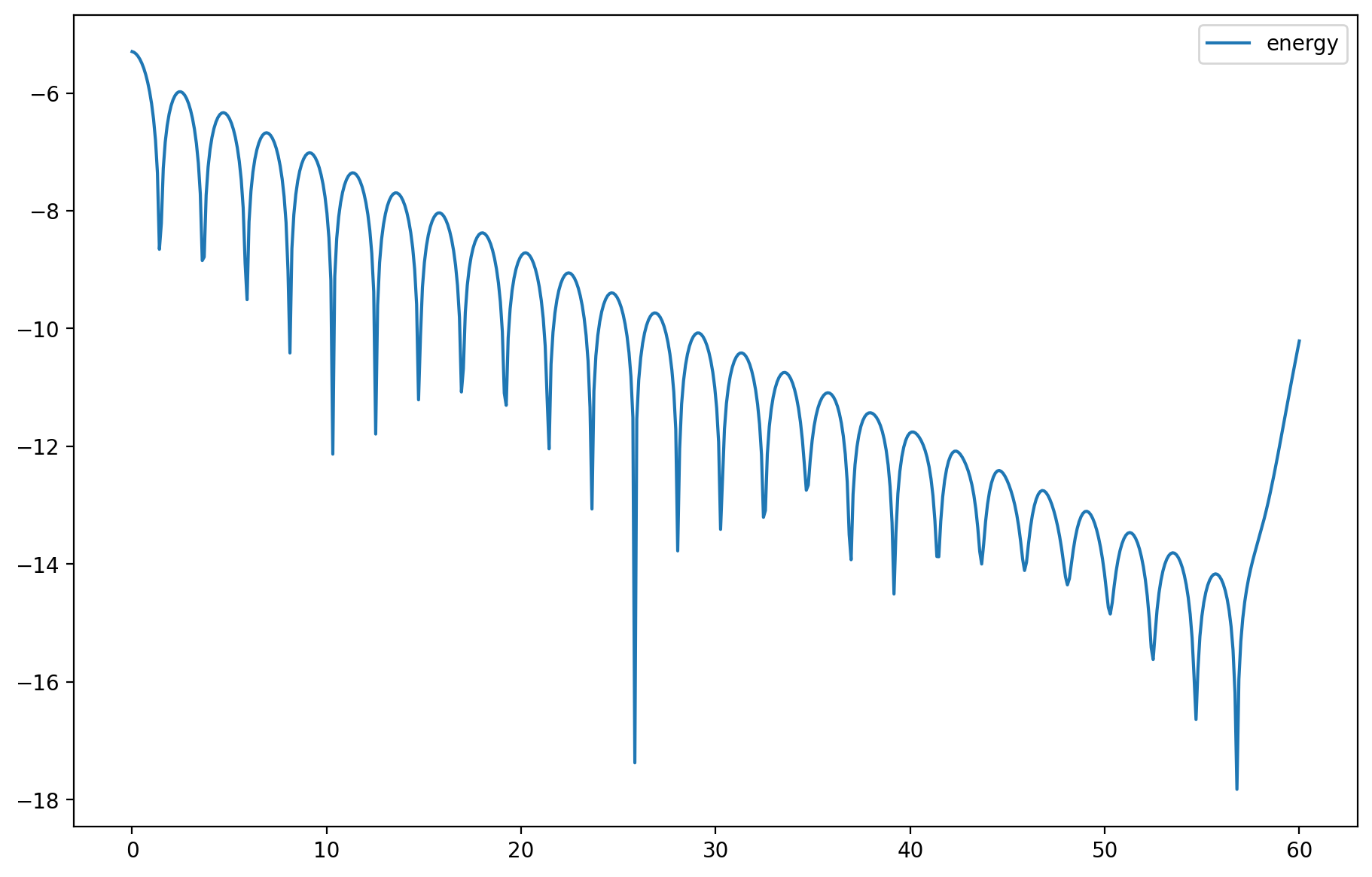
from time import time
elapsed_time = {}
fig, axes = plt.subplots()
# Set grid
nx, nv = 64, 64
xmin, xmax = 0.0, 4*np.pi
vmin, vmax = -6., 6.
# Create Vlasov-Poisson simulation
sim = VlasovPoissonThreaded(xmin, xmax, nx, vmin, vmax, nv)
# Initialize distribution function
X, V = np.meshgrid(sim.x, sim.v)
eps, kx = 0.001, 0.5
f = (1.0+eps*np.cos(kx*X))/np.sqrt(2.0*np.pi)* np.exp(-0.5*V*V)
f = np.asfortranarray(f)
# Set time domain
nstep = 600
t, dt = np.linspace(0.0, 60.0, nstep, retstep=True)
# Run simulation
etime = time()
nrj = sim.run(f, nstep, dt)
print(" elapsed time : {0:.4f} ".format(time()-etime))
# Plot energy
axes.plot(t, nrj, label='energy')
plt.legend();