Cython#
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10,6)
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
import numpy as np
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")

Cython provides extra syntax allowing for static type declarations (remember: Python is generally dynamically typed)
Python code gets translated into optimised C/C++ code and compiled as Python extension modules
Cython allows you to write fast C code in a Python-like syntax.
Furthermore, linking to existing C libraries is simplified.
Pure Python Function
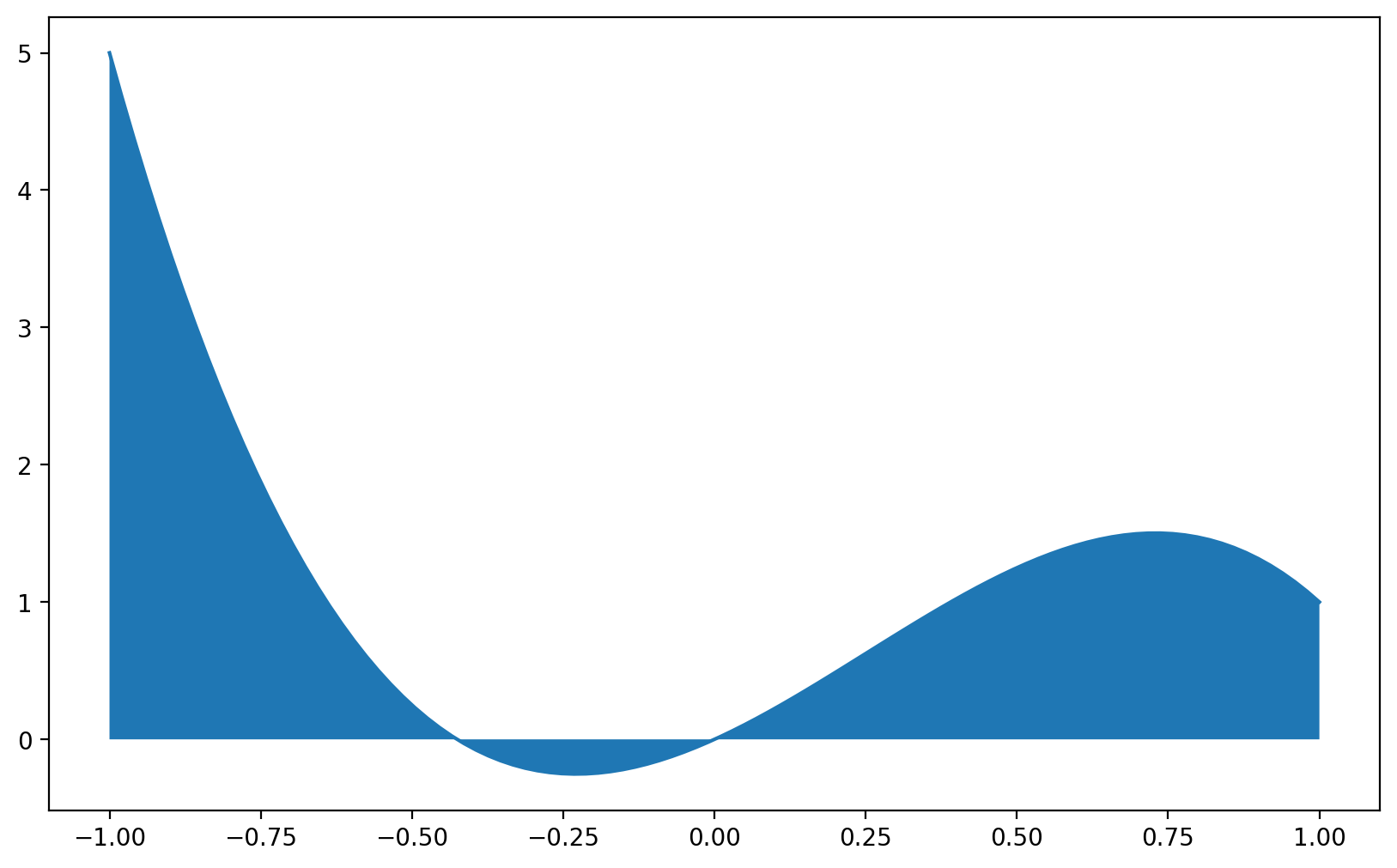
\(f(x)=-2x^3+5x^2+x\),
def f(x):
return -4*x**3 +3*x**2 +2*x
x = np.linspace(-1,1,100)
ax = plt.subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(x, f(x))
ax.fill_between(x, 0, f(x));
we compute integral \(\int_a^b f(x)dx\) numerically with \(N\) points.
def integrate_f_py(a,b,N):
s = 0
dx = (b - a) / (N-1)
for i in range(N-1): # we intentionally use the bad way to do this with a loop
x = a + i*dx
s += (f(x)+f(x+dx))/2
return s*dx
%timeit integrate_f_py(-1,1,10**3)
print(integrate_f_py(-1,1,1000))
461 μs ± 5.23 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000 loops each)
2.0000040080120174
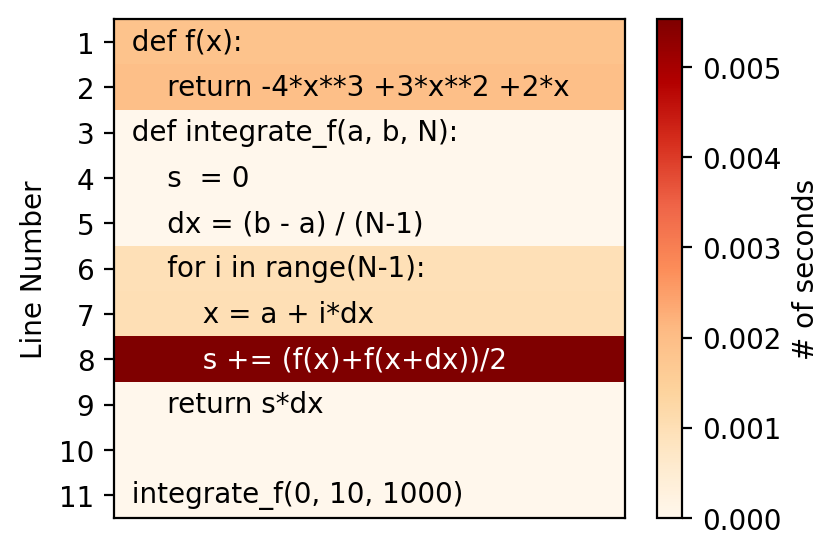
%load_ext heat
%%heat
def f(x):
return -4*x**3 +3*x**2 +2*x
def integrate_f(a, b, N):
s = 0
dx = (b - a) / (N-1)
for i in range(N-1):
x = a + i*dx
s += (f(x)+f(x+dx))/2
return s*dx
integrate_f(0, 10, 1000)
Pure C function
%%file integral_f_c.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#define NB_RUNS 1000
double f(double x) {
return -4*x*x*x +3*x*x +2*x;
}
double integrate_f_c(double a, double b, int N) {
double s = 0;
double dx = (b - a) / (N-1);
for(int i=0; i<N-1; ++i){
double x = a + i*dx;
s += (f(x)+f(x+dx))/2.0;
}
return s*dx;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
double a = atof(argv[1]);
double b = atof(argv[2]);
int N = atoi(argv[3]);
double res = 0;
clock_t begin = clock();
for (int i=0; i<NB_RUNS; ++i)
res += integrate_f_c( a, b, N );
clock_t end = clock();
fprintf( stdout, "integral_f(%3.1f, %3.1f, %d) = %f \n", a, b, N, res / NB_RUNS );
fprintf( stdout, "time = %e ms \n", (double)(end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC );
return 0;
}
Writing integral_f_c.c
!gcc -O3 integral_f_c.c; ./a.out -1 1 1000
integral_f(-1.0, 1.0, 1000) = 2.000004
time = 1.452000e-03 ms
Cython compilation: Generating C code#
Load Cython in jupyter notebook.
%load_ext Cython
C Variable and Type definitions#
In general, use cdef to declare C variables.
The command :
$ cython -a mycode.pyx
outputs an html file. It shows what parts of your code are C, which parts are Python, and where C-Python conversion occurs.
%%cython -a
cdef int i, j = 2, k = 3 # assigning values at declaration
i = 1 # assigning values afterwards
# avoid Python-C conversion! It's expensive:
a = 5
i = a
# same with C-Python conversion:
b = j
print("a = %d" % a)
print("i = %d" % i)
print("b = %d" % b)
a = 5
i = 5
b = 2
Generated by Cython 3.1.3
Yellow lines hint at Python interaction.
Click on a line that starts with a "+" to see the C code that Cython generated for it.
+01: cdef int i, j = 2, k = 3 # assigning values at declaration
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_9c069ec345b2765442cd655fd2d8007e8a508dbdf1d35ab3a29dfd7307c644fb_j = 2; __pyx_v_78_cython_magic_9c069ec345b2765442cd655fd2d8007e8a508dbdf1d35ab3a29dfd7307c644fb_k = 3; /* … */ __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_test, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+02: i = 1 # assigning values afterwards
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_9c069ec345b2765442cd655fd2d8007e8a508dbdf1d35ab3a29dfd7307c644fb_i = 1;
03: # avoid Python-C conversion! It's expensive:
+04: a = 5
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_a, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_5) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
+05: i = a
__Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_a); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyLong_As_int(__pyx_t_2); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_3 == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __pyx_v_78_cython_magic_9c069ec345b2765442cd655fd2d8007e8a508dbdf1d35ab3a29dfd7307c644fb_i = __pyx_t_3;
06: # same with C-Python conversion:
+07: b = j
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyLong_From_int(__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_9c069ec345b2765442cd655fd2d8007e8a508dbdf1d35ab3a29dfd7307c644fb_j); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 7, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_b, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 7, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+08: print("a = %d" % a)
__pyx_t_4 = NULL; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_builtin_print); __pyx_t_5 = __pyx_builtin_print; __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_6, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_a); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyUnicode_FormatSafe(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_kp_u_a_d, __pyx_t_6); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0; __pyx_t_8 = 1; { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[2] = {__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_7}; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_callargs+__pyx_t_8, (2-__pyx_t_8) | (__pyx_t_8*__Pyx_PY_VECTORCALL_ARGUMENTS_OFFSET)); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+09: print("i = %d" % i)
__pyx_t_5 = NULL; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_builtin_print); __pyx_t_7 = __pyx_builtin_print; __pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyLong_From_int(__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_9c069ec345b2765442cd655fd2d8007e8a508dbdf1d35ab3a29dfd7307c644fb_i); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(0, 9, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_6 = PyUnicode_Format(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_kp_u_i_d, __pyx_t_4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 9, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_8 = 1; { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[2] = {__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_6}; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_7, __pyx_callargs+__pyx_t_8, (2-__pyx_t_8) | (__pyx_t_8*__Pyx_PY_VECTORCALL_ARGUMENTS_OFFSET)); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 9, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+10: print("b = %d" % b)
__pyx_t_7 = NULL; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_builtin_print); __pyx_t_6 = __pyx_builtin_print; __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_b); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyUnicode_FormatSafe(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_kp_u_b_d, __pyx_t_5); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_t_8 = 1; { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[2] = {__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_4}; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_6, __pyx_callargs+__pyx_t_8, (2-__pyx_t_8) | (__pyx_t_8*__Pyx_PY_VECTORCALL_ARGUMENTS_OFFSET)); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
Another Python vs. Cython coloring guide#
%%cython -a
cdef int m, n
cdef double cy_total = 0.0
for m in range(10):
n = 2*m
cy_total += n
a, b = 0, 0
py_total = 0.0
for a in range(10):
b = 2*a
py_total += b
print(cy_total, py_total)
90.0 90.0
Generated by Cython 3.1.3
Yellow lines hint at Python interaction.
Click on a line that starts with a "+" to see the C code that Cython generated for it.
+01: cdef int m, n
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_test, __pyx_t_6) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
+02: cdef double cy_total = 0.0
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_cy_total = 0.0;
+03: for m in range(10):
for (__pyx_t_2 = 0; __pyx_t_2 < 10; __pyx_t_2+=1) {
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_m = __pyx_t_2;
+04: n = 2*m
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_n = (2 * __pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_m);
+05: cy_total += n
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_cy_total = (__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_cy_total + __pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_n); }
+06: a, b = 0, 0
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_0; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_4 = __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_0; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_4); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_a, __pyx_t_3) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_b, __pyx_t_4) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
+07: py_total = 0.0
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_py_total, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_0_0) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 7, __pyx_L1_error)
+08: for a in range(10):
for (__pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_t_5 < 10; __pyx_t_5+=1) {
__pyx_t_4 = PyLong_FromSsize_t(__pyx_t_5); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_a, __pyx_t_4) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
+09: b = 2*a
__Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_a); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(0, 9, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyLong_MultiplyCObj(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_2, __pyx_t_4, 2, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 9, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_b, __pyx_t_3) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 9, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
+10: py_total += b
__Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_py_total); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3); __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_b); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_6 = PyNumber_InPlaceAdd(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_py_total, __pyx_t_6) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 10, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0; }
+11: print(cy_total, py_total)
__pyx_t_4 = NULL; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_builtin_print); __pyx_t_3 = __pyx_builtin_print; __pyx_t_7 = PyFloat_FromDouble(__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_aff7a646bcbe78962cdde206a6e973a5a0d848c7fff020d1801fc2af7a9ab7bb_cy_total); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(0, 11, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7); __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_8, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_py_total); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_8)) __PYX_ERR(0, 11, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_9 = 1; { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[3] = {__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_8}; __pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_callargs+__pyx_t_9, (3-__pyx_t_9) | (__pyx_t_9*__Pyx_PY_VECTORCALL_ARGUMENTS_OFFSET)); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 11, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6); } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
%%cython -a
cdef struct Grail:
int age
float volume
cdef union Food:
char *spam
float *eggs
cdef enum CheeseType:
cheddar, edam,
camembert
cdef enum CheeseState:
hard = 1
soft = 2
runny = 3
cdef Grail holy
holy.age = 500
holy.volume = 10.0
print (holy.age, holy.volume)
500 10.0
Generated by Cython 3.1.3
Yellow lines hint at Python interaction.
Click on a line that starts with a "+" to see the C code that Cython generated for it.
+01: cdef struct Grail:
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_test, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; /* … */ struct __pyx_t_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_Grail { int age; float volume; };
02: int age
03: float volume
04: cdef union Food:
05: char *spam
06: float *eggs
+07: cdef enum CheeseType:
enum __pyx_t_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_CheeseType {
__pyx_e_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_cheddar,
__pyx_e_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_edam,
__pyx_e_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_camembert
};
08: cheddar, edam,
09: camembert
+10: cdef enum CheeseState:
enum __pyx_t_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_CheeseState {
__pyx_e_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_hard = 1,
__pyx_e_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_soft = 2,
__pyx_e_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_runny = 3
};
11: hard = 1
12: soft = 2
13: runny = 3
14: cdef Grail holy
+15: holy.age = 500
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_holy.age = 0x1F4;
+16: holy.volume = 10.0
__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_holy.volume = 10.0;
+17: print (holy.age, holy.volume)
__pyx_t_3 = NULL; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_builtin_print); __pyx_t_4 = __pyx_builtin_print; __pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyLong_From_int(__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_holy.age); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(0, 17, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_6 = PyFloat_FromDouble(__pyx_v_78_cython_magic_0d8a21f63911c4403fdaa9bcd3509858aceb1377309aebb778cba83f17d0a5e4_holy.volume); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 17, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_7 = 1; { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[3] = {__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_6}; __pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_callargs+__pyx_t_7, (3-__pyx_t_7) | (__pyx_t_7*__Pyx_PY_VECTORCALL_ARGUMENTS_OFFSET)); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 17, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
Cython Functions#
Use cdef to define a Cython function.
Cython function can accept either (inclusive) Python and C values as well as return either Python or C values,
Within a Cython module Python and Cython functions can call each other freely. However, only Python functions can be called from outside the module by Python code. (i.e. importing/exporting a Cython module into some Python code)
cpdef define a Cython function with a simple Python wrapper. However, when called from Cython the Cython / C code is called directly, bypassing the Python wrapper.
Writing pure code in Cython gives a small speed boost. Note that none of the code below is Cython-specific. Just add .pyx instead of .py extension.
%%file cython_f_example.pyx
def f(x):
return -4*x**3 +3*x**2 +2*x
def integrate_f(a, b, N):
s = 0
dx = (b - a) / (N-1)
for i in range(N-1):
x = a + i*dx
s += (f(x)+f(x+dx))/2
return s*dx
Writing cython_f_example.pyx
Cython Compilation#
The .pyx source file is compiled by Cython to a .c file.
The .c source file contains the code of a Python extension module.
The .c file is compiled by a C compiler to a .so (shared object library) file which can be imported directly into a Python session.
Build with CMake#
project(cython_f_example CXX)
include(UseCython) # Load Cython functions
# Set C++ output
set_source_file_properties(cython_f_example.pyx PROPERTIES CYTHON_IS_CXX TRUE )
# Build the extension module
cython_add_module( modname cython_f_example.pyx cython_f_example.cpp )
C/C++ generation with cython application#
cython -3 cython_f_example.pyx # create the C file for Python 3
cython -3 --cplus cython_f_example.pyx # create the C++ file for Python 3
build with a C/C++ compiler#
To build use the Makefile:
CC=gcc
CFLAGS=`python-config --cflags`
LDFLAGS=`python-config --ldflags`
cython_f_example:
${CC} -c $@.c ${CFLAGS}
${CC} $@.o -o $@.so -shared ${LDFLAGS}
Import the module in Python session
import cython_f_example
pyximport#
import Cython .pyx files as if they were .py files:
import pyximport
pyximport.install()
import cython_f_example
%timeit cython_f_example.integrate_f(-1,1,10**3)
print(cython_f_example.integrate_f(-1,1,1000))
390 μs ± 1.06 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000 loops each)
2.0000040080120174
Building a Cython module using distutils#
Create the setup.py script:
%%file setup.py
from distutils.core import setup
from Cython.Build import cythonize
setup(
name = 'Cython Example Integrate f Function',
ext_modules = cythonize("cython_f_example.pyx"),
)
Writing setup.py
%run setup.py build_ext --inplace --quiet
Compiling cython_f_example.pyx because it changed.
[1/1] Cythonizing cython_f_example.pyx
<Figure size 1000x600 with 0 Axes>
from cython_f_example import integrate_f
%timeit integrate_f(-1,1,10**3)
integrate_f(-1,1,10**3)
392 μs ± 1.8 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000 loops each)
2.0000040080120174
Why is it faster with Cython ?#
Python code is interpreted at every execution to machine code.
Compiled C code is already in machine code.
C is a statically-typed language. It gives to the compiler more information which allows it to optimize both computations and memory access.
To add two variables, Python checks the type before calling the right add function and store it to a value that can be new.
C just add the variables and return the result.
Add Cython types#
We coerce Python types to C types when calling the function. Still a “Python function” so callable from the global namespace.
%%cython
def f(x):
return -4*x**3 +3*x**2 +2*x
def cy_integrate_f(double a, double b, int N):
cdef int i
cdef double s, x, dx
s = 0
dx = (b - a) / (N-1)
for i in range(N-1):
x = a + i*dx
s += (f(x)+f(x+dx))/2
return s*dx
typing the iterator variable i with C semantics, tells Cython to compile the for-loop to pure C code.
typing a, s and dx is important as they are involved in arithmetic within the for-loop
Cython type declarations can make the source code less readable
Do not use them without good reason, i.e. only in performance critical sections.
%timeit cy_integrate_f(-1,1,10**3)
print(cy_integrate_f(-1,1,1000))
337 μs ± 192 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000 loops each)
2.0000040080120174
Finally, we integrate a Cython function instead of a Python function. This eliminates the Python-C conversion at the function call as seen above thus giving a pure Cython/C algorithm.
The primary downside is not being allowed to call
the function cy_f, from Python unless cpdef is used.
%%cython
cdef double cy_f(double x):
return -4*x**3 +3*x**2 +2*x
def cycy_integrate_f(double a, double b, int N):
cdef int i
cdef double s, x, dx
s = 0
dx = (b - a) / (N-1)
for i in range(N-1):
x = a + i*dx
s += (cy_f(x)+cy_f(x+dx))/2
return s*dx
%timeit cycy_integrate_f(-1,1,10**3)
print(cycy_integrate_f(-1,1,1000))
34 μs ± 88.9 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10,000 loops each)
2.0000040080120174
Exercise : Cythonize the trivial exponential function.#
%%cython -a
def exp_python(x,terms=50):
sum = 0.
power = 1.
fact = 1.
for i in range(terms):
sum += power/fact
power *= x
fact *= i+1
return sum
Generated by Cython 3.1.3
Yellow lines hint at Python interaction.
Click on a line that starts with a "+" to see the C code that Cython generated for it.
+1: def exp_python(x,terms=50):
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_1exp_python(PyObject *__pyx_self,
#if CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL
PyObject *const *__pyx_args, Py_ssize_t __pyx_nargs, PyObject *__pyx_kwds
#else
PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds
#endif
); /*proto*/
static PyMethodDef __pyx_mdef_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_1exp_python = {"exp_python", (PyCFunction)(void(*)(void))(__Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCallWithKeywords)__pyx_pw_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_1exp_python, __Pyx_METH_FASTCALL|METH_KEYWORDS, 0};
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_1exp_python(PyObject *__pyx_self,
#if CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL
PyObject *const *__pyx_args, Py_ssize_t __pyx_nargs, PyObject *__pyx_kwds
#else
PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds
#endif
) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_x = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_v_terms = 0;
#if !CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL
CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t __pyx_nargs;
#endif
CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *const *__pyx_kwvalues;
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("exp_python (wrapper)", 0);
#if !CYTHON_METH_FASTCALL
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_SIZE
__pyx_nargs = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args);
#else
__pyx_nargs = PyTuple_Size(__pyx_args); if (unlikely(__pyx_nargs < 0)) return NULL;
#endif
#endif
__pyx_kwvalues = __Pyx_KwValues_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, __pyx_nargs);
{
PyObject ** const __pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_x,&__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_terms,0};
PyObject* values[2] = {0,0};
const Py_ssize_t __pyx_kwds_len = (__pyx_kwds) ? __Pyx_NumKwargs_FASTCALL(__pyx_kwds) : 0;
if (unlikely(__pyx_kwds_len) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
if (__pyx_kwds_len > 0) {
switch (__pyx_nargs) {
case 2:
values[1] = __Pyx_ArgRef_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 1);
if (!CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && unlikely(!values[1])) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1:
values[0] = __Pyx_ArgRef_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 0);
if (!CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && unlikely(!values[0])) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 0: break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
const Py_ssize_t kwd_pos_args = __pyx_nargs;
if (__Pyx_ParseKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_kwvalues, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values, kwd_pos_args, __pyx_kwds_len, "exp_python", 0) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
if (!values[1]) values[1] = __Pyx_NewRef(((PyObject *)((PyObject*)__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_50)));
for (Py_ssize_t i = __pyx_nargs; i < 1; i++) {
if (unlikely(!values[i])) { __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("exp_python", 0, 1, 2, i); __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error) }
}
} else {
switch (__pyx_nargs) {
case 2:
values[1] = __Pyx_ArgRef_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 1);
if (!CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && unlikely(!values[1])) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1:
values[0] = __Pyx_ArgRef_FASTCALL(__pyx_args, 0);
if (!CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && unlikely(!values[0])) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
if (!values[1]) values[1] = __Pyx_NewRef(((PyObject *)((PyObject*)__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_50)));
}
__pyx_v_x = values[0];
__pyx_v_terms = values[1];
}
goto __pyx_L6_skip;
__pyx_L5_argtuple_error:;
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("exp_python", 0, 1, 2, __pyx_nargs); __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_L6_skip:;
goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done;
__pyx_L3_error:;
for (Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp=0; __pyx_temp < (Py_ssize_t)(sizeof(values)/sizeof(values[0])); ++__pyx_temp) {
Py_XDECREF(values[__pyx_temp]);
}
__Pyx_AddTraceback("_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39.exp_python", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return NULL;
__pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:;
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_exp_python(__pyx_self, __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_terms);
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
/* function exit code */
for (Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp=0; __pyx_temp < (Py_ssize_t)(sizeof(values)/sizeof(values[0])); ++__pyx_temp) {
Py_XDECREF(values[__pyx_temp]);
}
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_exp_python(CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_x, PyObject *__pyx_v_terms) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_sum = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_power = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_fact = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_i = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
/* … */
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_CyFunction_New(&__pyx_mdef_78_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d11c2dc17fe48dec0611a19715d5cb058693c8fcb0156f39_1exp_python, 0, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_exp_python, NULL, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_cython_magic_8b465f382b3ed9d6d1, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, ((PyObject *)__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_codeobj_tab[0])); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_CyFunction_SetDefaultsTuple(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_tuple[0]);
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_exp_python, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_d, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_n_u_test, __pyx_t_2) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+2: sum = 0.
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_0_);
__pyx_v_sum = __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_0_;
+3: power = 1.
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_1_);
__pyx_v_power = __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_1_;
+4: fact = 1.
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_1_);
__pyx_v_fact = __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_float_1_;
+5: for i in range(terms):
__pyx_t_2 = NULL; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_builtin_range); __pyx_t_3 = __pyx_builtin_range; __pyx_t_4 = 1; { PyObject *__pyx_callargs[2] = {__pyx_t_2, __pyx_v_terms}; __pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_FastCall(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_callargs+__pyx_t_4, (2-__pyx_t_4) | (__pyx_t_4*__Pyx_PY_VECTORCALL_ARGUMENTS_OFFSET)); __Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); } if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_t_1)) || PyTuple_CheckExact(__pyx_t_1)) { __pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_1; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_t_6 = NULL; } else { __pyx_t_5 = -1; __pyx_t_3 = PyObject_GetIter(__pyx_t_1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_6 = (CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_LIMITED_API) ? PyIter_Next : __Pyx_PyObject_GetIterNextFunc(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0; for (;;) { if (likely(!__pyx_t_6)) { if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_t_3))) { { Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp = __Pyx_PyList_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_3); #if !CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_SIZE if (unlikely((__pyx_temp < 0))) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) #endif if (__pyx_t_5 >= __pyx_temp) break; } __pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyList_GetItemRef(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_5); ++__pyx_t_5; } else { { Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp = __Pyx_PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_3); #if !CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_SIZE if (unlikely((__pyx_temp < 0))) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) #endif if (__pyx_t_5 >= __pyx_temp) break; } #if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS __pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_NewRef(PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_5)); #else __pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_5); #endif ++__pyx_t_5; } if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) } else { __pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_6(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) { PyObject* exc_type = PyErr_Occurred(); if (exc_type) { if (unlikely(!__Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(exc_type, PyExc_StopIteration))) __PYX_ERR(0, 5, __pyx_L1_error) PyErr_Clear(); } break; } } __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); __Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_i, __pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0; /* … */ } __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
+6: sum += power/fact
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(__pyx_v_power, __pyx_v_fact); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_2 = PyNumber_InPlaceAdd(__pyx_v_sum, __pyx_t_1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 6, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_sum, __pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+7: power *= x
__pyx_t_2 = PyNumber_InPlaceMultiply(__pyx_v_power, __pyx_v_x); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 7, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_power, __pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
+8: fact *= i+1
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyLong_AddObjC(__pyx_v_i, __pyx_mstate_global->__pyx_int_1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_1 = PyNumber_InPlaceMultiply(__pyx_v_fact, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 8, __pyx_L1_error) __Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1); __Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0; __Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_fact, __pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
+9: return sum
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_sum); __pyx_r = __pyx_v_sum; goto __pyx_L0;
%timeit exp_python(1.,50)
3.21 μs ± 32.4 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100,000 loops each)
%%cython
# %load solutions/cython/exponential.pyx
#cython: profile=False
#cython: cdivision=True
def exp_cython(double x, int terms = 50):
cdef double sum
cdef double power
cdef double fact
cdef int i
sum = 0.
power = 1.
fact = 1.
for i in range(terms):
sum += power/fact
power *= x
fact *= i+1
return sum
%timeit exp_cython(1.,50)
109 ns ± 0.145 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10,000,000 loops each)
Cython and Numpy#
The Numpy library contains many fast numerics routines. Their speed comes from manipulating the low-level C-arrays that the numpy.array object wraps rather than computing over slow Python lists. Using Cython one can access those low-level arrays and implement their own fast algorithms while allowing the easy interaction afforded by Python + Numpy.
The examples below are various implementations of the naive matrix multiplication algorithm. We will start with a pure Python implementation and then incrementally add structures that allow Cython to exploit the low-level speed of the numpy.array object.
Pure Python implementation compiled in Cython without specific optimizations.#
%%cython
def matmul1(A, B, out=None):
assert A.shape[1] == B.shape[0]
for i in range(A.shape[0]):
for j in range(B.shape[1]):
s = 0
for k in range(A.shape[1]):
s += A[i,k] * B[k,j]
out[i,j] = s
return out
Import numpy as a Cython module#
We now take advantage of the ability to access the underlying C arrays in the numpy.array object from Cython, thanks to a special numpy.pxd file included with Cython. (The Cython developers worked closely with Numpy developers to make this optimal.)
To begin with, we have to cimport numpy: that is, import numpy as a Cython module rather than a Python module. To do so, simply type:
cimport numpy as np
Another important thing to note is the type of Numpy indexers. There is a special Numpy variable type used for numpy.array indices called Py_ssize_t. To take full advantage of the speedups that Cython can provide we should make sure to type the variables used for indexing as such.
%%cython
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
ctypedef np.float64_t dtype_t # shorthand type. easy to change
def matmul2(np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2] A,
np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2] B,
np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2] out=None):
cdef Py_ssize_t i, j, k
cdef dtype_t s
assert A.shape[1] == B.shape[0]
for i in range(A.shape[0]):
for j in range(B.shape[1]):
s = 0
for k in range(A.shape[1]):
s += A[i,k] * B[k,j]
out[i,j] = s
return out
Content of stderr:
In file included from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarraytypes.h:1913,
from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarrayobject.h:12,
from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/arrayobject.h:5,
from /home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b8fb140bf941deb06cc24b20cedcdcce62a1e12900f2c4ce165dc9f687e19e01.c:1149:
/home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/npy_1_7_deprecated_api.h:17:2: warning: #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " "#define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION" [-Wcpp]
17 | #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " \
| ^~~~~~~
import numpy as np
from timeit import timeit
A = np.random.random_sample((64,64))
B = np.random.random_sample((64,64))
C = np.zeros((64,64))
%timeit matmul1(A,B,C)
62.9 ms ± 245 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
%timeit matmul2(A,B,C)
268 μs ± 5.92 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1,000 loops each)
Tuning indexing#
The array lookups are still slowed down by two factors:
Bounds checking is performed.
Negative indices are checked for and handled correctly.
The code doesn’t use negative indices, and always access to arrays within bounds. We can add a decorator to disable bounds checking:
%%cython
cimport cython # cython tools
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
ctypedef np.float64_t dtype_t
@cython.boundscheck(False) # turn off bounds-checking for entire function
@cython.wraparound(False) # turn off negative index wrapping for entire function
def matmul3(np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2] A,
np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2] B,
np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2] out=None):
cdef Py_ssize_t i, j, k
cdef dtype_t s
assert A.shape[1] == B.shape[0]
for i in range(A.shape[0]):
for j in range(B.shape[1]):
s = 0
for k in range(A.shape[1]):
s += A[i,k] * B[k,j]
out[i,j] = s
return out
Content of stderr:
In file included from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarraytypes.h:1913,
from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarrayobject.h:12,
from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/arrayobject.h:5,
from /home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_47b859b5a1396d8f275daf537de9047e018dc954643bc399a90d0054e6d06724.c:1150:
/home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/npy_1_7_deprecated_api.h:17:2: warning: #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " "#define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION" [-Wcpp]
17 | #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " \
| ^~~~~~~
%timeit matmul3(A,B,C)
186 μs ± 137 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10,000 loops each)
Cython Build Options#
boundcheck(True,False) : array bounds checking
wraparound(True,False) : negative indexing.
initializedcheck(True,False): checks that a memoryview is initialized
nonecheck(True,False) : Check if one argument is None
overflowcheck(True,False) : Check if int are too big
cdivision(True,False) : If False, adjust the remainder and quotient operators C types to match those of Python ints. Could be very effective when it is set to True.
profile (True / False) : Write hooks for Python profilers into the compiled C code. Default is False.
Numpy objects with external C program.#
Note that this can actually be slower because the C function is not the best implementation of matrix multiplication. Call cblas with same technique is an interesting exercise.
%%file mydgemm.c
void my_dgemm( int m, int n, int k,
double a[m][n], double b[n][k], float c[m][k] )
{
double ab = 0;
for( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++ ) {
for( int i = 0 ; i < k ; i++ ) {
for( int l = 0 ; l < n ; l++ ){
ab += a[j][l] * b[l][i];
}
c[j][i] = ab ;
ab = 0;
}
}
}
Writing mydgemm.c
The
np.ndarray[double, ndim=2, mode="c"]assures that you get a C-contiguous numpy array of doublesThe
&input[0,0]passed in the address of the beginning of the data array.
from pyximport import install
import os
here = os.getcwd()
%%cython -I {here}
# do not forget to change the file path
cdef extern from "mydgemm.c":
void my_dgemm (int m, int n, int k,
double *A, double *B, double *C)
cimport cython
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
ctypedef np.float64_t dtype_t
@cython.boundscheck(False)
@cython.wraparound(False)
def matmul4(np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2, mode="c"] A,
np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2, mode="c"] B,
np.ndarray[dtype_t, ndim=2, mode="c"] C=None):
cdef int m = A.shape[0]
cdef int n = A.shape[1]
cdef int k = B.shape[1]
cdef dtype_t s
my_dgemm(m, n, k, &A[0,0], &B[0,0], &C[0,0])
return C
Content of stderr:
In file included from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarraytypes.h:1913,
from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/ndarrayobject.h:12,
from /home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/arrayobject.h:5,
from /home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd.c:1154:
/home/runner/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/numpy/_core/include/numpy/npy_1_7_deprecated_api.h:17:2: warning: #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " "#define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION" [-Wcpp]
17 | #warning "Using deprecated NumPy API, disable it with " \
| ^~~~~~~
/home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd.c: In function '__pyx_pf_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_matmul4':
/home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd.c:4912:46: error: passing argument 4 of 'my_dgemm' from incompatible pointer type [-Wincompatible-pointer-types]
4912 | my_dgemm(__pyx_v_m, __pyx_v_n, __pyx_v_k, (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_1, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_2, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.diminfo[1].strides))), (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_3, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_4, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.diminfo[1].strides))), (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.diminfo[1].strides))));
| ~^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
| |
| __pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t * {aka double *}
In file included from /home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd.c:1148:
/home/runner/work/python-notebooks/python-notebooks/notebooks/mydgemm.c:2:22: note: expected 'double (*)[n]' but argument is of type '__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *' {aka 'double *'}
2 | double a[m][n], double b[n][k], float c[m][k] )
| ~~~~~~~^~~~~~~
/home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd.c:4912:318: error: passing argument 5 of 'my_dgemm' from incompatible pointer type [-Wincompatible-pointer-types]
4912 | my_dgemm(__pyx_v_m, __pyx_v_n, __pyx_v_k, (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_1, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_2, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.diminfo[1].strides))), (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_3, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_4, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.diminfo[1].strides))), (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.diminfo[1].strides))));
| ~^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
| |
| __pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t * {aka double *}
/home/runner/work/python-notebooks/python-notebooks/notebooks/mydgemm.c:2:38: note: expected 'double (*)[k]' but argument is of type '__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *' {aka 'double *'}
2 | double a[m][n], double b[n][k], float c[m][k] )
| ~~~~~~~^~~~~~~
/home/runner/.cache/ipython/cython/_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd.c:4912:590: error: passing argument 6 of 'my_dgemm' from incompatible pointer type [-Wincompatible-pointer-types]
4912 | my_dgemm(__pyx_v_m, __pyx_v_n, __pyx_v_k, (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_1, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_2, __pyx_pybuffernd_A.diminfo[1].strides))), (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_3, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_4, __pyx_pybuffernd_B.diminfo[1].strides))), (&(*__Pyx_BufPtrCContig2d(__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.rcbuffer->pybuffer.buf, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.diminfo[0].strides, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_pybuffernd_C.diminfo[1].strides))));
| ~^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
| |
| __pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t * {aka double *}
/home/runner/work/python-notebooks/python-notebooks/notebooks/mydgemm.c:2:53: note: expected 'float (*)[k]' but argument is of type '__pyx_t_78_cython_magic_b4a53c5b6a5915356e5414c9fab0ed3d1b7b1814401b718393262325aa017abd_dtype_t *' {aka 'double *'}
2 | double a[m][n], double b[n][k], float c[m][k] )
| ~~~~~~^~~~~~~
%timeit matmul4(A,B,C)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[37], line 1
----> 1 get_ipython().run_line_magic('timeit', 'matmul4(A,B,C)')
File ~/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py:2504, in InteractiveShell.run_line_magic(self, magic_name, line, _stack_depth)
2502 kwargs['local_ns'] = self.get_local_scope(stack_depth)
2503 with self.builtin_trap:
-> 2504 result = fn(*args, **kwargs)
2506 # The code below prevents the output from being displayed
2507 # when using magics with decorator @output_can_be_silenced
2508 # when the last Python token in the expression is a ';'.
2509 if getattr(fn, magic.MAGIC_OUTPUT_CAN_BE_SILENCED, False):
File ~/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/IPython/core/magics/execution.py:1226, in ExecutionMagics.timeit(self, line, cell, local_ns)
1224 for index in range(0, 10):
1225 number = 10 ** index
-> 1226 time_number = timer.timeit(number)
1227 if time_number >= 0.2:
1228 break
File ~/miniconda3/envs/runenv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/IPython/core/magics/execution.py:184, in Timer.timeit(self, number)
182 gc.disable()
183 try:
--> 184 timing = self.inner(it, self.timer)
185 finally:
186 if gcold:
File <magic-timeit>:1, in inner(_it, _timer)
NameError: name 'matmul4' is not defined
Exercise : Find prime numbers < 10000#
# %load solutions/cython/is_prime0.py
def is_prime0(n):
if n < 4: return True
if n % 2 == 0 : return False
k = 3
while k*k <= n:
if n % k == 0: return False
k += 2
return True
[ p for p in range(20) if is_prime0(p)]
L = list(range(10000))
%timeit [ p for p in L if is_prime0(p)]
%%cython
def is_prime1(n):
if n < 4: return True
if n % 2 == 0 : return False
k = 3
while k*k <= n:
if n % k == 0: return False
k += 2
return True
[ p for p in range(20) if is_prime1(p)]
%timeit [p for p in L if is_prime1(p)]
Add Cython types without modifying the Python Code#
%%cython
import cython
@cython.locals(n=int, k=int)
def is_prime2(n):
if n < 4: return True
if n % 2 == 0 : return False
k = 3
while k*k <= n:
if n % k == 0: return False
k += 2
return True
[ p for p in range(20) if is_prime2(p)]
%timeit [p for p in L if is_prime2(p) ]
Cython function#
%%cython
import cython
cdef bint is_prime3(int n):
if n < 4: return True
if n % 2 == 0: return False
cdef int k = 3
while k*k <= n:
if n % k == 0: return False
k += 2
return True
def prime_list(L):
return [p for p in L if is_prime3(p)]
prime_list(list(range(20)))
%timeit prime_list(L)
%%cython
import cython
from numpy cimport ndarray
import numpy
cdef bint is_prime3(int n):
if n < 4: return True
if n % 2 == 0: return False
cdef int k = 3
while k*k <= n:
if n % k == 0: return False
k += 2
return True
def prime_array(ndarray[int, ndim=1] L):
cdef ndarray[int, ndim=1] res = ndarray(shape=(L.shape[0]),dtype=numpy.int32)
cdef int i
for i in range(L.shape[0]):
res[i] = is_prime3(L[i])
return L[res==1]
import numpy as np
prime_array(np.arange(20,dtype=np.int32))
npL = numpy.array(L,dtype=np.int32)
%timeit prime_array(npL)
Using Parallelism#
Cython supports native parallelism via OpenMP
by default, Python’s Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) prevents that several threads use the Python interpreter simultaneously
to use this kind of parallelism, the GIL must be released
If you have a default compiler with openmp support you can use this magic command in your notebook.
%%cython --compile-args=-fopenmp --link-args=-fopenmp
%%file cython_omp.pyx
import cython
from cython.parallel cimport parallel, prange # import parallel functions
import numpy as np
from numpy cimport ndarray
cdef bint is_prime4(int n) nogil: #release the gil
if n < 4: return True
if n % 2 == 0: return False
cdef int k = 3
while k*k <= n:
if n % k == 0: return False
k += 2
return True
@cython.boundscheck(False)
def prime_array_omp(ndarray[int, ndim=1] L):
cdef ndarray[int, ndim=1] res = ndarray(shape=(L.shape[0]),dtype=np.int32)
cdef Py_ssize_t i
with nogil, parallel(num_threads=4):
for i in prange(L.shape[0]): #Parallel loop
res[i] = is_prime4(L[i])
return L[res==1]
To use the OpenMP support, you need to enable OpenMP. For gcc this can be done as follows in a setup.py:
%%file setup.py
from distutils.core import setup
from distutils.extension import Extension
from Cython.Build import cythonize
import os, sys
import numpy
if sys.platform == "darwin": # for omp, use gcc installed with brew
os.environ["CC"]="gcc-10"
os.environ["CXX"]="g++-10"
ext_modules = [
Extension(
"cython_omp",
["cython_omp.pyx"],
extra_compile_args=['-fopenmp'],
extra_link_args=['-fopenmp'],
include_dirs=[numpy.get_include()]
)
]
setup(
name='Cython OpenMP Example',
ext_modules=cythonize(ext_modules),
)
# python setup.py build_ext --inplace
%run setup.py build_ext --inplace --quiet
from cython_omp import prime_array_omp
prime_array_omp(np.arange(20,dtype=np.int32))
%timeit prime_array_omp(npL)
References#
Kurt W. Smith